What Is Manual Handing?
 It is often thought that manual handling is simply lifting and carrying boxes. However, the definition of manual handling states:
It is often thought that manual handling is simply lifting and carrying boxes. However, the definition of manual handling states:
“The transporting or supporting of a load by hand or bodily force, including pushing, pulling, lifting, lowering, sliding and/or repetitive movements”.
If manual handling tasks are carried out in a work place environment this is covered by law by the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 and The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (amended in 2002).
The aim of Health and Safety Legislation is to prevent accident and injury in the workplace. The Health & Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 applies to all workplaces in the UK. It describes the general principles for health and safety at work, including the employer’s duty of care. As well, it is an Enabling Act, which allows other more specific regulations to be made under it (i.e. Manual Handling Operations Regulations, Management of H& S Regulations).
Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (amended in 2002)
 The main duties of employers under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations are:
The main duties of employers under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations are:
- Avoid all needs for manual handling activities as much as reasonably possible.
- Assess any risk of injury resulting from manual handling which is unavoidable.
- Reduce the risk of injury as much as possible.
Equally, the employee’s responsibilities are:
- Follow the stated workplace actions to ensure safety.
- Utilise any equipment provided for your safety.
- Co-operate with your employer on health and safety issues.
Please note that there is no maximum weight limit specified in the regulations. The Enforcing Authorities believe that it is more efficient to adopt an ergonomic approach to manual handling, as to impose weight limit restrictions would prove problematic.
The Spine
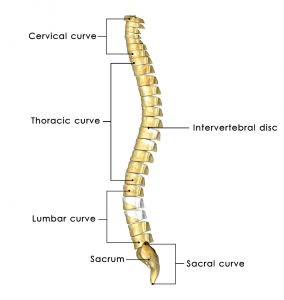 The spine is the part of the body that suffers the biggest impact from manual handling operations. It supports the whole body, including the skull and consists of 4 defined curves (i.e. it is not straight, like commonly thought):
The spine is the part of the body that suffers the biggest impact from manual handling operations. It supports the whole body, including the skull and consists of 4 defined curves (i.e. it is not straight, like commonly thought):
- The Cervical (Neck) Curve.
- The Thoracic (Chest) Curve.
- The Lumbar (Lower back) Curve.
- The Sacrum (Tailbone) Curve.
It is the lumbar region of the spine which takes the most strain and therefore the area most back injuries occur from manual handling activities.
The spine consists of ligaments which connect each vertebrae, these are secured by intervertebral discs which act as soft ‘cushions’ of tissue which protect the bones and allow movement.